TWiki Webmaster Reference (ver. 01 Sep 2001)
This page contains all documentation topics as one long and complete reference sheet. Use the extended menu below to jump directly to sections. Doubleclick anywhere on-screen to return to the top of the page. (You can also browse the TWiki reference as individual pages from the full topics menu.)On this page:
Note: Read the most up to date version of this document at http://TWiki.org/cgi-bin/view/TWiki/TWikiDocumentation- TWiki Webmaster Reference (ver. 01 Sep 2001)
- TWiki Access Control
- An Important Control Consideration
- Permissions settings of the webs on this TWiki site
- Authentication vs. Access Control
- Users and Groups
- Restricting Access
- Controlling access to a Web
- Controlling access to a Topic
- Allowing public access to specific topics in a restricted web
- Empty values in access control variables
- Securing File Attachments
- Controlling who can manage top-level webs
- How TWiki evaluates ALLOW/DENY settings
- Allowing web creation by user mapping manager
- User masquerading
- Dynamic access control
- Access control and INCLUDE
- Customizing "access denied" message
- Custom user/group notations
- Access Control quick recipes
- Configuring access control for topics of a certain name in all webs
- TWiki Templates
- TWiki Skins
- TWiki Variables
- TWiki Meta Data
- TWiki Plugins
Warning: Can't find topic TWiki.TWikiImplementationNotes
Warning: Can't find topic TWiki.TWikiInstallationNotes
Warning: Can't find topic TWiki.TWikiUpgradeNotes
Warning: Can't find topic TWiki.TWikiAuthentication
TWiki Access Control
Restricting read and write access to topics and webs, by Users and groups TWiki Access Control allows you restrict access to single topics and entire webs, by individual user and by user Groups. Access control, combined with TWikiUserAuthentication, lets you easily create and manage an extremely flexible, fine-grained privilege system.An Important Control Consideration
Your organization will learn that, while fostering an open collaborative environment, soft security (peer review), together with version control (complete audit trail) will take care of any security concern you might have. Open, free-form editing is the essence of WikiCulture - what makes TWiki different and often more effective than other collaborative environments. For that reason, it is strongly recommended that decisions to restrict read or write access to a web or a topic are made with great care - the more restrictions, the less wiki in the mix. Experience shows that unrestricted write access works very well because:- Peer influence is enough to ensure that only relevant content is posted.
- Peer editing - the ability for anyone to rearrange all content on a page - keeps topics focused.
- In TWiki, content is transparently preserved under revision control:
- Edits can easily be rolled back to a previous revision if needed.
- Users are encouraged to edit and refactor (condense a long topic), since there's a safety net.
- Create broad-based Groups (for more and varied input), and...
- Avoid creating view-only topics (if you can read it, you should be able to contribute to it).
Permissions settings of the webs on this TWiki site
| Web | Sitemap | VIEW | CHANGE | RENAME | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Listed | DENY | ALLOW | DENY | ALLOW | DENY | ALLOW | |
| |
on | TWikiAdminGroup, TWikiRegistrationAgent, AAOGeneralGroup | TWikiAdminGroup, AAOGeneralGroup | ||||
| |
on | TWikiAdminGroup | TWikiAdminGroup | ||||
| |
on | * | TWikiAdminGroup, AAOGeneralGroup | * | TWikiAdminGroup | ||
- A blank in the the above table may mean either the corresponding control is absent or commented out or that it has been set to a null value. The two conditions have dramatically different and possibly opposed semantics.
- TWikiGuest is the guest account - used by unauthenticated users.
- The TWiki web must not deny view to TWikiGuest; otherwise, people will not be able to register.
Authentication vs. Access Control
Authentication: Identifies who a user is based on a login procedure. See TWikiUserAuthentication. Access control: Restrict access to content based on users and groups once a user is identified.Users and Groups
Access control is based on the familiar concept of Users and Groups. Users are defined by their WikiNames. They can then be organized in unlimited combinations by inclusion in one or more user Groups. For convenience, Groups can also be included in other Groups.Managing Users
A user can create an account in TWikiRegistration. The following actions are performed:- WikiName and encrypted password are recorded using the password manager if authentication is enabled.
- A confirmation e-mail is sent to the user.
- A user profile page with the WikiName of the user is created in the Main web.
- The user is added to the TWikiUsers topic.
Managing Groups
The following describes the standard TWiki support for groups. Your local TWiki may have an alternate group mapping manager installed. Check with your TWiki administrator if you are in doubt. Groups are defined by group topics located in theMain web. To create a new group, visit TWikiGroups and enter the name of the new group ending in Group into the "new group" form field. This will create a new group topic with two important settings: -
Set GROUP = < list of Users and/or Groups > -
Set ALLOWTOPICCHANGE = < list of Users and/or Groups >
-
Set GROUP = SomeUser, OtherUser, SomeGroup
-
Set ALLOWTOPICCHANGE = MarketingGroup
The Super Admin Group
A number of TWiki functions (for example, renaming webs) are only available to administrators. Administrators are simply users who belong to the SuperAdminGroup. This is a standard user group, the name of which is defined by {SuperAdminGroup} setting in configure. The default name of this group is theTWikiAdminGroup. The system administrator may have chosen a different name for this group if your local TWiki uses an alternate group mapping manager but for simplicity we will use the default name TWikiAdminGroup in the rest of this topic.
You can create new administrators simply by adding them to the TWikiAdminGroup topic. For example, -
Set GROUP = RobertCailliau, TimBernersLee
Restricting Access
You can define who is allowed to read or write to a web or a topic. Note that some plugins may not respect access permissions.- Restricting VIEW blocks viewing and searching of content. When you restric VIEW to a topic or web, this also restricts INCLUDE and Formatted SEARCH from showing the content of the topics.
- Restricting CHANGE blocks creating new topics, changing topics or attaching files.
- Restricting RENAME prevents renaming of topics within a web.
Controlling access to a Web
You can define restrictions on who is allowed to view a TWiki web. You can restrict access to certain webs to selected Users and Groups, by:- authenticating all webs and restricting selected webs: Topic access in all webs is authenticated, and selected webs have restricted access.
- authenticating and restricting selected webs only: Provide unrestricted viewing access to open webs, with authentication and restriction only on selected webs.
- You can define these settings in the WebPreferences topic, preferable towards the end of the topic:
-
Set DENYWEBVIEW = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set ALLOWWEBVIEW = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set DENYWEBCHANGE = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set ALLOWWEBCHANGE = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set DENYWEBRENAME = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set ALLOWWEBRENAME = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups >
-
-
Set ALLOWWEBVIEW = Main.MarketingGroup
ALLOWWEBVIEW set, this will also apply to the subweb. Also note that you will need to ensure that the parent web's FINALPREFERENCES does not include the access control settings listed above. Otherwise you will not be able override the parent web's access control settings in sub-webs.
Creation and renaming of sub-webs is controlled by the WEBCHANGE setting on the parent web (or ROOTCHANGE for root webs). Renaming is additionally restricted by the setting of WEBRENAME in the web itself.
Note: If you restrict access to the Main, make sure to add the TWikiRegistrationAgent so that users can register. Example: -
Set ALLOWWEBCHANGE = TWikiAdminGroup, TWikiRegistrationAgent
Controlling access to a Topic
- You can define these settings in any topic, preferable towards the end of the topic:
-
Set DENYTOPICVIEW = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set ALLOWTOPICVIEW = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set DENYTOPICCHANGE = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set ALLOWTOPICCHANGE = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set DENYTOPICRENAME = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set ALLOWTOPICRENAME = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups >
-
-
Set ALLOWTOPICVIEW = Main.MarketingExecGroup
Allowing public access to specific topics in a restricted web
You may want to completely open up access to a specific topic within a restricted web - allowing access by anybody. There is a special group for that - Main.AllUsersGroup. The following setting allows view access to the topic by anybody even if they are not authenticated.-
Set ALLOWTOPICVIEW = Main.AllUsersGroup
-
Set ALLOWTOPICVIEW = Main.AllAuthUsersGroup
-
Set ALLOWTOPICOPERATION = Main.AllUsersGroup
tools/eliminate_emptydenytopic is provided.
After upgrading from pre 6.0 to post 6.0, you need to run it.
Empty values in access control variables
Setting an empty value to an access control variable is the same as not setting at all:-
Set ALLOWTOPICVIEW =
Securing File Attachments
By default, TWiki does not secure file attachments. Without making the following changes to the twiki.conf file, it is possible for anyone who has access to the server to gain access to an attachment if they know the attachment's fully qualified path, even though access to the topic associated with the attachment is secured. This is because attachments are referred to directly by Apache, and are not by default delivered via TWiki scripts. This means that the above instructions for controlling to topics do not apply to attachments unless you make the changes as described below. An effective way to secure attachments is to apply the same access control settings to attachments as those applied to topics. This security enhancement can be accomplished by instructing the webserver to redirect accesses to attachments via the TWikiviewfile script, which honors the TWiki access controls settings to topics. See the notes below for implications.
The preferred method to secure attachments is by editing the twiki.conf file to include:
ScriptAlias /do /filesystem/path/to/twiki/bin
Alias /pub/TWiki /filesystem/path/to/twiki/pub/TWiki
Alias /pub/Sandbox /filesystem/path/to/twiki/pub/Sandbox
ScriptAlias /pub /filesystem/path/to/twiki/bin/viewfile
Notes: - It is recommended to use TWiki:TWiki/ApacheConfigGenerator
 to generate the Apache config file for your TWiki.
to generate the Apache config file for your TWiki.
- You will need to restart your Apache server after this change.
- Images embedded in topics will load slower since attached images will also be delivered by the
viewfilescript. The TWiki web and Sandbox web are excluded for performance reasons. - The
viewfilescript sets the mime type based upon file name suffix. Unknown types are served as text/plain which can result in corrupt files.
Controlling who can manage top-level webs
Top level webs are a special case, because they don't have a parent web with a WebPreferences. So there has to be a special control just for the root level.- You can define these settings in the Main.TWikiPreferences topic, preferable towards the end of the topic:
-
Set DENYROOTCHANGE = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups > -
Set ALLOWROOTCHANGE = < comma-delimited list of Users and Groups >
-
ROOTCHANGE access to rename an existing top-level web. You just need WEBCHANGE in the web itself.
How TWiki evaluates ALLOW/DENY settings
When deciding whether to grant access, TWiki evaluates the following rules in order (read from the top of the list; if the logic arrives at PERMITTED or DENIED that applies immediately and no more rules are applied). You need to read the rules bearing in mind that VIEW, CHANGE and RENAME access may be granted/denied separately.- If the user is an administrator
- access is PERMITTED.
- If DENYTOPIC is set to a list of wikinames
- people in the list will be DENIED.
- If DENYTOPIC is set to empty ( i.e.
Set DENYTOPIC =)- the access control setting is ignored.
 Attention: The spec changed in TWiki-6.0; access was permitted in earlier TWiki releases.
Attention: The spec changed in TWiki-6.0; access was permitted in earlier TWiki releases.
- the access control setting is ignored.
- If ALLOWTOPIC is set
- people in the list are PERMITTED
- everyone else is DENIED
- If DENYWEB is set to a list of wikinames
- people in the list are DENIED access
- If ALLOWWEB is set to a list of wikinames
- people in the list will be PERMITTED
- everyone else will be DENIED
- If you got this far, access is PERMITTED
Allowing web creation by user mapping manager
There are cases where DENYROOTCHANGE, ALLOWROOTCHANGE, DENYWEBCHANGE, and ALLOWWEBCHANGE, and DENYWEBCHANGE are not capable enough to implement web creation permission you want. To cope with such cases, when a new web is created, thecanCreateWeb($cUID, $web) method of the user mapping manager is called if the method exists.
If it returns true, TWiki goes ahead and create the web without checking access control variables.
Please read AllowWebCreateByUserMappingManager for more details.
User masquerading
There are cases where it's handy to access TWiki on behalf of somebody else retaining a trace of your real identity rather than completely becoming a different user. We call it user masquerading. TWiki provides a framework to implement that. Please read UserMasquerading for more information. This is an advanced feature and not many TWiki sites are using, but there is a part in the following section mentioning it, it's mentioned here.Dynamic access control
There are pitfalls and you need to harden your web to avoid unexpected access. Before using this feature, please read this entire section through carefully. You may want to restrict access dynamically -- based on topic name, a form field value, or some combination of factors. To cope with such situations, the dynamic access control mechanism is provided. If you setDYNAMIC_ACCESS_CONTROL 'on' at WebPreferences of the web, TWiki variables in access control variables mentioned above are expanded.
Example 1 - restriction based on topic name
Let's assume you need to restrict changes only to the CroniesGroup members except with topics whose name ends with Public, which need be changed by anybody. That is achieve by the following settings on WebPrefences.
* Set DYNAMIC_ACCESS_CONTROL = on
* Set ALLOWWEBCHANGE = %IF{"'%CALCULATE{$SUBSTRING(%TOPIC%, -6, 6)}%' = 'Public'" then="%WIKINAME%" else="CroniesGroup"}%
Example 2 - restriction based on form field
Let's assume:- a web storing requests on topics whose name starts with ReqEnt
- Each request topic has a form field "Requestor", which has the wiki name of the requestor
- Users can view only requests they created
- The members of the SupportGroup mail group can view all requests
* Set DYNAMIC_ACCESS_CONTROL = on
* Set ALLOWWEBVIEW = %IF{"'%CALCULATE{$SUBSTRING(%TOPIC%, 1, 6)}%' = 'ReqEnt' and '%FORMFIELD{Requestor}%' != '%WIKINAME%'" then="SupportGroup" else="%WIKINAME%"}%
Specifically the following access control variables are subject to TWiki variable expansion in their values. - DENYTOPIC* (e.g. DENYTOPICVIEW, DENYTOPICCHANGE)
- ALLOWTOIPC*
- DENYWEB*
- ALLOWWEB*
Dynamic access control in accessing a different web's topic
Let's assume WebA has the following lines on WebPreferences.* Set DYNAMIC_ACCESS_CONTROL = on * Set MEMBERS = JaneSmith, JoeSchmoe * Set ALLOWWEBVIEW = %MEMBERS%This is not a good way to use dynamic access control but it does restrict access only to those listed in MEMBERS. However, access control doesn't work as expected when WebA.TopicB is accessed from WebC.TopicD by
%INCLUDE{WebA.TopicB}% or other variables.
This is because %MEMBERS% is defined in WebA and may have a different value in other webs.
You may think the following lines cheat the access control on WebA but actually not.
* Set MEMBERS = %WIKINAME%
%INCLUDE{WebA.TopicB}%
This is because when a topic (e.g. WebC.TopicD) is accessed from browser and the topic refers to another topic in a different web (e.g. WebA.TopicB) and the different web employs dynamic access control, access to another topic is defined being on the safer side.
Topic level dynamic access control
On a topic, it's possible to use a variable defined on the topic for topic level access restriction. E.g.* Set MEMBERS = JaneSmith, JoeSchmoe * Set ALLOWTOPICVIEW = %MEMBERS%[This is not a good way to use dynamic access control
Dynamic access control and user masquerading
Your user mapping handler may be providing the UserMasquerading feature. In that case, you expect dynamic access control to just work when user masquerading is in effect. Otherwise, you cannot test if your dynamic access control configuration is working as expected on your own. Dynamic access control does work as expected even if user masquerading is in effect. For that, the following things are happening under the hood. Let's think about Example 2 mentioned above. When you masquerading as SomebodyElse, you need to be able to see SomebodyElse's requests only. In the access control setting, a form field value is compared with %WIKINAME%. While user masquerading is in effect, your wiki name is YourNameOnBehalfOfSomebodyElse. It cannot match the form field value. To make dynamic access control work under these circumstances, variable expansion for dynamic access control is skewed as follows. Specifically, the following variables are expanded to the value of SomeboyElse's rather than YourNameOnBehalfOfSomebodyElse's.- WIKINAME
- USERNAME
- WIKIUSERNAME
Avoiding vulnerability
By default, user level preferences are read before web level preferences. This means a user can set a preferences variable at the user level and finalise it. To prevent this sort of attack, you need to harden your web or site by disabling user preferences by e.g. having the following line onlib/LocalSite.cfg
$TWiki::cfg{DemoteUserPreferences}= 1;
and having the following line on your WebPreferences and then finalise DENYUSERPREFEENCES.
* Set DENYUSERPREFEENCES = allPlease read TWikiVariables#ControllingUserLevelPrefsOverride for details. Again by default, predefined variables such as
%IF{...}% can be overridden by preferences variables.
If user preferences are disabled, ordinary users cannot attack using user preferences, but topic level preferences may cause unexpected consequences.
As such, all predefined variables need to be made un-overridable by having the following line on WebPreferences and then finalise OVERRIDABLEPREDEFINEDVARIABLES.
* Set OVERRIDABLEPREDEFINEDVARIABLES =Please read TWikiVariables#PredefinedVariables for details.
Disabling dynamic access control
You may not be comfortable with dynamic access control because it may slow things down. Or you may not want to be bothered by questions raised by users about it. If so, you can disable it by setting DYNAMIC_ACCESS_CONTROL 'off' and then finalizing at the local site level. (cf. TWikiVariables#Setting_Preferences_Variables)Access control and INCLUDE
ALLOWTOPICVIEW and ALLOWTOPICCHANGE only applies to the topic in which the settings are defined. If a topic A includes another topic B, topic A does not inherit the access rights of the included topic B. Examples: Topic A includes topic B- If the included topic B has ALLOWTOPICCHANGE set to block editing for a user, it does not prevent editing the including topic A.
- If the included topic B has ALLOWTOPICVIEW set to block view for a user, the user can still view topic A but he cannot see the included topic B. He will see a message No permission to view B
Customizing "access denied" message
When access is denied, a page as follows is displayed: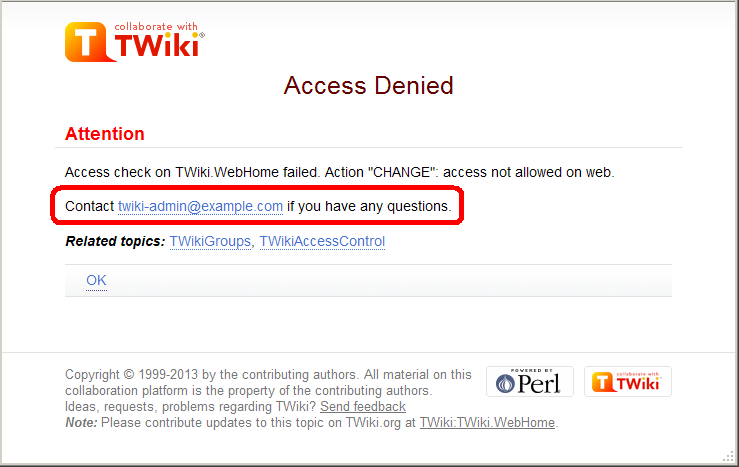 You may want to customize the passage annotated in the red rectangle.
For example, with a web restricting access, you may want to show the link to an access request form.
You can achieve that by setting
You may want to customize the passage annotated in the red rectangle.
For example, with a web restricting access, you may want to show the link to an access request form.
You can achieve that by setting TOPIC_ACCESS_CONTACT varialbe on WebPreferences. e.g.
* Set TOPIC_ACCESS_CONTACT = If you need to access this site, please apply [[Main.AccessForm][here]]Please note that setting it on a topic other than WebPreferences does not take effect. This is a limitation of the current implementation.
Custom user/group notations
You can have custom user/group notations such asUSER:userid and LDAPGROUP:group-name and use them for access control. For example:
* Set ALLOWWEBCHANGE = UID:buzz, LDAPGROUP:foo-barIn a large organization, TWiki may need to depend on user and group data provided by its infrastructure. Custom user/group notations are handy in such situations though it's not trivial to implement. Please read here for details.
Access Control quick recipes
Restrict Access to Whole TWiki Site
In a firewalled TWiki, e.g. an intranet wiki or extranet wiki, you want to allow only invited people to access your TWiki. There are three options: 1. Install TWiki Behind Firewall: The firewall takes care of giving access to TWiki to authorized people only. This is a typical setup for a company wiki. As for TWiki configuration, no special setup is needed. 2. Extranet TWiki Using Template Login: All TWiki content (pages and attachments) need to be access controlled. The Template Login allows users to login and logout. Only logged in users can access TWiki content. Configuration: Follow the default setup, then change these configure settings:- Secure attachments as documented. The TWiki:TWiki.ApacheConfigGenerator
 is useful to get the setting right.
is useful to get the setting right.
- Require authentication for all TWiki scripts except
backuprestore,configure,login,logonandresetpasswdwith the following configure setting:
$TWiki::cfg{AuthScripts} = 'attach, changes, edit, manage, oops, preview, rdiff, rdiffauth, register, rename, rest, save, search, twiki_cgi, upload, statistics, view, viewauth, viewfile'; - When you install additional plugins make sure to add scripts they might introduce also to
twiki/binalso to the{AuthScripts}configure setting.
Attention: Some scripts of additional plugins might not be aware of TWiki's template login. Test all new scripts with a non-authenticated user!
twiki/bin and twiki/pub directories to all but valid users. In the Apache config file for TWiki (twiki.conf or .htaccess), replace the <FilesMatch "(attach|edit|... section with this:
<FilesMatch ".*">
require valid-user
</FilesMatch>
Notes:
- In all three options, content can be restricted selectively with ALLOWWEBVIEW and other access control settings documented above. See also the next quick recipe.
- In the extranet setup, someone with access to the site needs to register new users. If you still want public users to be able to register automatically follow TWiki:TWiki.RegisterOnViewRestrictedSite
 .
.
Authenticate and Restrict Selected Webs Only
Use the following setup to provide unrestricted viewing access to open webs, with authentication only on selected webs. Requires TWikiUserAuthentication to be enabled.- Restrict view access to selected Users and Groups. Set one or both of these variables in its WebPreferences topic:
-
Set DENYWEBVIEW = < list of Users and Groups > -
Set ALLOWWEBVIEW = < list of Users and Groups > - Note:
DENYWEBVIEWis evaluated beforeALLOWWEBVIEW. Access is denied if the authenticated person is in theDENYWEBVIEWlist, or not in theALLOWWEBVIEWlist. Access is granted ifDENYWEBVIEWandALLOWWEBVIEWare not defined.
-
Hide Control Settings
Edit topic preference settings under More topic actions menu. Preferences set in this manner are not visible in the topic text, but take effect nevertheless. Access control settings added as topic preference settings are stored in the topic meta data and they override settings defined in the topic text.
Alternatively, place them in HTML comment markers, but this exposes the access setting during ordinary editing.
<!--
* Set DENYTOPICCHANGE = Main.SomeGroup
-->
Obfuscating Webs
Another way of hiding webs is to keep them hidden by not publishing the URL and by preventing theall webs search option from accessing obfuscated webs. Do so by enabling the NOSEARCHALL variable in WebPreferences: -
Set NOSEARCHALL = on
Read-only Skin Mode
It is possible to turn the PatternSkin and TopMenuSkin into read-only mode by removing the edit and attach controls (links and buttons). This is mainly useful if you have TWiki application pages or dashboards where you do not want regular users to change content. The read-only skin mode is not a replacement for access control; you can use it in addition to access control. Details at PatternSkinCustomization#ReadOnlySkinMode.Configuring access control for topics of a certain name in all webs
You may need to restrict access to topics of a certain name in all webs. For example, there might be an add-on refering to a certain topic of all webs. And the add-on does things only administrators are supposed to do. In that case, change to the topic needs to be restricted only to administrators and must not be overridable. Let's say there is AutomationAddOn which refers to WebAutomation of all webs. And WebAutomation needs to be modifable only by administrators. That can be achieved by the following configuration.
$TWiki::cfg{Access}{Topic}{WebAutomation} = {
DENYCHANGE => 'Main.AllUsersGroup',
};
In addition to ALLOWCHANGE, you can sepcify DENYCHANGE, ALLOWVIEW, DENYVIEW, ALLOWRENAME, and DENYRENAME as follows.
$TWiki::cfg{Access}{Topic}{SpecialTopic} = {
DENYVIEW => 'JoeSchmoe',
ALLOWVIEW => 'FooGroup',
};
$TWiki::cfg{Access}{Topic}{TOPICNAME} has precedence over DENYTOPIC* and ALLOWTOPIC*.
For example, if the configuration for WebAutomation is there as above, there is no way to allow non-adminsitrators to change the WebAutomation topic of any web.
As a way to configure access control, this may look crude.
The reason why configured this way is that this can be part of plugin/add-on/contrib's configuration.
For example, Config.spec of AutomationAddOn would have the following lines, with which proper access control to WebAutomation topics is implemented without the administrator knowing it.
$TWiki::cfg{Access}{Topic}{WebAutomation} = {
DENYCHANGE => 'Main.AllUsersGroup',
};
TWiki Templates
Definition of the templates used to render all HTML pages displayed in TWikiOverview
Templates are plain text with embedded template directives that tell TWiki how to compose blocks of text together, to create something new. There are two types of template:- Master Templates: Define the HTML used to display TWiki pages.
- Template Topics: Define default text when you create a new topic
Master Templates
TWiki uses master templates when composing the output from all actions, like topic view, edit, and preview. This allows you to change the look and feel of all pages by editing just a few template files. Master templates are also used in the definition of TWikiSkins. Master templates are stored as text files with the extension.tmpl.
They are usually HTML with embedded template directives.
The directives are expanded when TWiki wants to generate a user interface screen.
How Template Directives Work
- Directives are of the form
%TMPL:<key>%and%TMPL:<key>{"attr"}%. - Directives:
-
%TMPL:INCLUDE{"file"}%: Includes a template file. The file is found as described below. -
%TMPL:DEF{"block"}%: Define a block. All text between this and the next%TMPL:END%directive is removed and saved for later use with%TMPL:P. -
%TMPL:END%: Ends a block definition. -
%TMPL:P{"var"}%: Includes a previously defined block. -
%{...}%: is a comment.
-
- Two-pass processing lets you use a variable before or after declaring it.
- Templates and TWikiSkins work transparently and interchangeably. For example, you can create a skin that overloads only the
twiki.tmplmaster template, liketwiki.print.tmpl, that redefines the header and footer. -
 Use of template directives is optional: templates work without them.
Use of template directives is optional: templates work without them.
-
 NOTE: Template directives work only for templates: they do not get processed in normal topic text.
NOTE: Template directives work only for templates: they do not get processed in normal topic text.
%TMPL:DEF{"x"}% x%P%z%TMPL:END% then %TMPL:P{"x" P="y"}% will expand to xyz.
Note that parameters can simply be ignored; for example, %TMPL:P{"x"}% will expand to x%P%z.
Any alphanumeric characters can be used in parameter names.
You are highly recommended to use parameter names that cannot be confused with TWikiVariables.
Note that three parameter names, context, then and else are reserved.
They are used to support a limited form of "if" condition that you can use to select which of two templates to use, based on a context identifier:
%TMPL:DEF{"link_inactive"}%<input type="button" disabled value="Link>%TMPL:END%
%TMPL:DEF{"link_active"}%<input type="button" onclick="link()" value="Link" />%TMPL:END%
%TMPL:P{context="inactive" then="inactive_link" else="active_link"}% for %CONTEXT%
When the "inactive" context is set, then this will expand the "link_inactive" template; otherwise it will expand the "link_active" template.
See IfStatements for details of supported context identifiers.
Finding Templates
The master templates shipped with a twiki release are stored in the twiki/templates directory. As an example,twiki/templates/view.tmpl is the default template file for the twiki/bin/view script.
You can save templates in other directories as long as they are listed in the {TemplatePath} configuration setting.
The {TemplatePath} is defined in the Miscellaneous section of the configure page.
You can also save templates in user topics (IF there is no possible template match in the templates directory).
The {TemplatePath} configuration setting defines which topics will be accepted as templates.
Templates that are included with an explicit '.tmpl' extension are looked for only in the templates/ directory.
For instance %TMPL:INCLUDE{"example.tmpl"}% will only return templates/example.tmpl, regardless of {TemplatePath} and SKIN settings.
The out-of-the-box setting of {TemplatePath} supports the following search order to determine which template file or topic to use for a particular script or %TMPL:INCLUDE{"script"}% statement.
The skin path is set as described in TWikiSkins.
- templates/web/script.skin.tmpl for each skin on the skin path
-
 this usage is supported for compatibility only and is deprecated. Store web-specific templates in TWiki topics instead.
this usage is supported for compatibility only and is deprecated. Store web-specific templates in TWiki topics instead.
-
- templates/script.skin.tmpl for each skin on the skin path
- templates/web/script.tmpl
-
 this usage is supported for compatibility only and is deprecated. Store web-specific templates in TWiki topics instead.
this usage is supported for compatibility only and is deprecated. Store web-specific templates in TWiki topics instead.
-
- templates/script.tmpl
- The TWiki topic aweb.atopic if the template name can be parsed into aweb.atopic
- The TWiki topic web.SkinSkinScriptTemplate for each skin on the skin path
- The TWiki topic web.ScriptTemplate
- The TWiki topic %SYSTEMWEB%.SkinSkinScriptTemplate for each skin on the skin path
- The TWiki topic %SYSTEMWEB%.ScriptTemplate
- script refers to the script name, e.g
view,edit - Script refers to the same, but with the first character capitalized, e.g
View - skin refers to a skin name, e.g
dragon,pattern. All skins are checked at each stage, in the order they appear in the skin path. - Skin refers to the same, but with the first character capitalized, e.g
Dragon - web refers to the current web
example template file will be searched for in the following places, when the current web is Thisweb and the skin path is print,pattern:
-
templates/Thisweb/example.print.tmpldeprecated; don't rely on it -
templates/Thisweb/example.pattern.tmpldeprecated; don't rely on it -
templates/example.print.tmpl -
templates/example.pattern.tmpl -
templates/Thisweb/example.tmpldeprecated; don't rely on it -
templates/example.tmpl -
Thisweb.PrintSkinExampleTemplate -
Thisweb.PatternSkinExampleTemplate -
Thisweb.ExampleTemplate -
TWiki.PrintSkinExampleTemplate -
TWiki.PatternSkinExampleTemplate -
TWiki.ExampleTemplate
view and edit scripts, for example when a topic-specific template is required. Two preference variables can be used to override the templates used: -
VIEW_TEMPLATEsets the template to be used for viewing a topic -
EDIT_TEMPLATEsets the template for editing a topic.
view and edit respectively. The template search order is as specified above.
{TemplatePath} so that another directory, such as the %USERSWEB% appears at the front. You can then put your own templates into that directory or web and these will override the standard templates. (Note that such will increase the lookup time for templates by searching your directory first.)
TMPL:INCLUDE recursion for piecewise customization, or mixing in new features
If there is recursion in the TMPL:INCLUDE chain (eg twiki.classic.tmpl contains%TMPL:INCLUDE{"twiki"}%, the templating system will include the next twiki.SKIN in the skin path.
For example, to create a customization of pattern skin, where you only want to over-ride the breadcrumbs for the view script, you can create only a view.yourlocal.tmpl:
%TMPL:INCLUDE{"view"}%
%TMPL:DEF{"breadcrumb"}% We don't want any crumbs %TMPL:END%
and then set SKIN=yourlocal,pattern
The default {TemplatePath} will not give you the desired result if you put these statements in the topic Thisweb.YourlocalSkinViewTemplate. The default {TemplatePath} will resolve the request to the template/view.pattern.tmpl, before it gets to the Thisweb.YourlocalSkinViewTemplate resolution. You can make it work by prefixing the {TemplatePath} with: $web.YourlocalSkin$nameTemplate.
Default master template
twiki.tmpl is the default master template. It defines the following sections.
| Template variable: | Defines: |
|---|---|
%TMPL:DEF{"sep"}% |
"|" separator |
%TMPL:DEF{"htmldoctype"}% |
Start of all HTML pages |
%TMPL:DEF{"standardheader"}% |
Standard header (ex: view, index, search) |
%TMPL:DEF{"simpleheader"}% |
Simple header with reduced links (ex: edit, attach, oops) |
%TMPL:DEF{"standardfooter"}% |
Footer, excluding revision and copyright parts |
Template Topics
The second type of template in TWiki are template topics. Template topics define the default text for new topics. There are four types of template topic:| Topic Name: | What it is: |
|---|---|
| WebTopicViewTemplate | Alert page shown when you try to view a nonexistent topic. This page is usually used as a prompt to help you create a new topic. |
| WebTopicNonWikiTemplate | Alert page shown when you try to view a nonexistent topic with a non-WikiName. Again, this page is used as a prompt to help you create the new topic. |
| WebTopicEditTemplate | Default text used in a new topic. |
| <MyCustomNamed>Template | Whenever you create a topic ending in the word "Template", it is automatically added to the list of available templates in the "Use Template" drop down field on the WebCreateNewTopic page. |
edit script, TWiki locates a topic to use as a content template according to the following search order: - A topic name specified by the
templatetopicCGI parameter- if no web is specified, the current web is searched first and then the TWiki web
- WebTopicEditTemplate in the current web
- WebTopicEditTemplate in the Main web
- WebTopicEditTemplate in the TWiki web
Variable Expansion
TWikiVariables located in template topics get expanded as follows when a new topic is created.1. Default variable expansion
The following variables used in a template topic automatically get expanded when new topic is created based on it:| Variable: | Description: |
|---|---|
%DATE% |
Signature format date. See VarDATE |
%GMTIME% |
Date/time. See VarGMTIME |
%GMTIME{...}% |
Formatted date/time. See VarGMTIME2 |
%NOP% |
A no-operation variable that gets removed. Useful to prevent a SEARCH from hitting an edit template topic; also useful to escape a variable, such as %URLPA%NOP%RAM{...}% escaping URLPARAM |
%STARTSECTION{type="templateonly"}% |
Text that gets removed when a new topic based on the template is created. See notes below. |
%SERVERTIME% |
Date/time. See VarSERVERTIME |
%SERVERTIME{...}% |
Formatted date/time. See VarSERVERTIME2 |
%USERNAME% |
Login name of user who is instantiating the new topic, e.g. guest |
%URLPARAM{"name"}% |
Value of a named URL parameter. See VarURLPARAM. |
%WIKINAME% |
WikiName of user who is instantiating the new topic, e.g. TWikiGuest |
%WIKIUSERNAME% |
User name of user who is instantiating the new tpoic, e.g. Main.TWikiGuest |
2. Preventing variable expansion
In a template topic, embed text that you do not want expanded inside a%STARTSECTION{type="templateonly"}% ... %ENDSECTION{type="templateonly"}% section. For example, you might want to write this in the template topic:
%STARTSECTION{type="templateonly"}%
This template can only be changed by:
* Set ALLOWTOPICCHANGE = Main.TWikiAdminGroup
%ENDSECTION{type="templateonly"}%
This will restrict who can edit the template topic, but will be removed when a new topic based on that template topic is created.
%NOP% can be used to prevent expansion of TWiki variables that would otherwise be expanded during topic creation. For example, escape %SERVERTIME% with %SER%NOP%VERTIME%.
3. Causing variable expansion in a section
You can forcefully expand TWikiVariables by placing them inside atype="expandvariables" section in the template topic, such as:
...Example: If you have the following content in a template topic:
* %SYSTEMWEB%.ATasteOfTWiki - view a short introductory presentation on TWiki for beginners * %SYSTEMWEB%.WelcomeGuest - starting points on TWiki * %SYSTEMWEB%.TWikiUsersGuide - complete TWiki documentation * Sandbox.%HOMETOPIC% - try out TWiki on your own * Sandbox.%TOPIC%Sandbox - just for meyou will get this raw text in new topics based on that template topic:
* TWiki.ATasteOfTWiki - view a short introductory presentation on TWiki for beginners * TWiki.WelcomeGuest - starting points on TWiki * TWiki.TWikiUsersGuide - complete TWiki documentation * Sandbox.WebHome - try out TWiki on your own * Sandbox.JimmyNeutronSandbox - just for me
4. Specifying variables to be expanded individually
You may want to mix variables to be expanded and variables not to be. By prepending a variable name withEOTC__ (EOTC followed by two underscores; EOTC stands for Expand On Topic Creation), you can have the variable expanded.
Here's an example.
%EOTC__SEARCH{"."
topic="%URLPARAM{prefix}%*"
nonoise="on"
format="$percntINCLUDE{$topic}$percnt" separator="$n"
}%
This yields a series of %INCLUDE{...}%s, which are not expanded.
This is not achievable by an expandvariables section.
Specifying a Form
When you create a new topic based on a template, you often want the new topic to have a form attached to it. You can attach a form to the template topic, in which case it will be copied into the new topic. Sometimes this isn't quite what you want, as it copies all the existing data from the template topic into the new topic. To avoid this and use the default values specified in the form definition instead, you can use theformtemplate CGI parameter to the edit script to specify the name of a form to attach.
See TWikiScripts for information about all the other parameters to edit.
Automatically Generated Topic Names
For TWiki applications it is useful to be able to automatically generate unique topic names, such as BugID0001, BugID0002, etc. You can addAUTOINC<n> to the topic name in the edit and save scripts, and it will be replaced with an auto-incremented number on topic save. <n> is a number starting from 0, and may include leading zeros. Leading zeros are used to zero-pad numbers so that auto-incremented topic names can sort properly. Deleted topics are not re-used to ensure uniqueness of topic names. That is, the auto-incremented number is always higher than the existing ones, even if there are gaps in the number sequence.
Examples: -
BugAUTOINC0- creates topic namesBug0,Bug1,Bug2, ... (does not sort properly) -
ItemAUTOINC0000- creates topic namesItem0000,Item0001,Item0002, ... (sorts properly up to 9999) -
DocIDAUTOINC10001- start withDocID10001,DocID10002, ... (sorts properly up to 99999; auto-links)
AUTOINC<n> are preserved, but are not taken into account when calculating the next increment. Use this to create topic names that have a unique identifier (serial number) and a descriptive text.
Example: -
BlogAUTOINC0001-my-first-blog- creates topic nameBlog0001-my-first-blog -
BlogAUTOINC0001-my-crazy-cats- creates topic nameBlog0002-my-crazy-cats -
BlogAUTOINC0001-fondue-recipe- creates topic nameBlog0003-fondue-recipe
[[%SCRIPTURLPATH{edit}%/%WEB%/BugIDAUTOINC00001?templatetopic=BugTemplate;topicparent=%TOPIC%;t=%SERVERTIME{"$day$hour$min$sec"}%][Create new item]]
Template Topics in Action
Here is an example for creating new topics (in the Sandbox web) based on a specific template topic and form: The above form asks for a topic name. A hidden input tag namedtemplatetopic specifies ExampleTopicTemplate as the template topic to use. Here is the raw text of the form:
%EDITFORMFIELD{ "new" type="start" action="edit" topic="Sandbox.%TOPIC%" }%
* New example topic:
%EDITFORMFIELD{ "topic" type="text" value="ExampleTopicAUTOINC0001" size="30" }%
%EDITFORMFIELD{ "templatetopic" type="hidden" value="%SYSTEMWEB%.ExampleTopicTemplate" }%
%EDITFORMFIELD{ "topicparent" type="hidden" value="%HOMETOPIC%" }%
%EDITFORMFIELD{ "onlywikiname" type="hidden" value="on" }%
%EDITFORMFIELD{ "onlynewtopic" type="hidden" value="on" }%
%EDITFORMFIELD{ "form" type="submit" value="Create" }%
%EDITFORMFIELD{ "form" type="end" }%
Here is the equivalent form using a hand-crafted HTML form:
<form name="new" action="%SCRIPTURLPATH{edit}%/Sandbox/%HOMETOPIC%">
* New example topic:
<input type="text" name="topic" value="ExampleTopicAUTOINC0001" size="30" />
<input type="hidden" name="templatetopic" value="%SYSTEMWEB%.ExampleTopicTemplate" />
<input type="hidden" name="topicparent" value="%HOMETOPIC%" />
<input type="hidden" name="onlywikiname" value="on" />
<input type="hidden" name="onlynewtopic" value="on" />
<input type="submit" class="twikiSubmit" value="Create" />
</form>
save script instead of the edit script in the form action. When you specify the save script in an HTML form tag you have to use the "post" method. This is done automatically when using the EDITFORMFIELD variable. Example when using the HTML form tag:
<form name="new" action="%SCRIPTURLPATH{save}%/Sandbox/" method="post">
...
</form>
edit and save scripts understand many more parameters, see TWikiScripts#edit and TWikiScripts#save for details.
%WIKIUSERNAME% and %DATE% variables in your topic templates to include the signature of the person creating a new topic. The variables are expanded into fixed text when a new topic is created. The standard signature is: -- %WIKIUSERNAME% - %DATE%
Using Absolute vs Relative URLs in Templates
When you use TWikiVariables such as %PUBURL% and %PUBURLPATH% in templates you should be aware that using %PUBURL% instead of %PUBURLPATH% puts absolute URLs in the produced HTML. This means that when a user saves a TWiki page in HTML and emails the file to someone outside a company firewall, the receiver has a severe problem viewing it. It is therefore recommended always to use the %PUBURLPATH% to refer to images, CSS, Javascript files etc so links become relative. This way browsers just give up right away and show a usable html file. Related Topics: TWikiSkins, TWikiForms, TWikiScripts, DeveloperDocumentationCategory, AdminDocumentationCategoryTWiki Skins
A skin overlays regular templates to provide specific look and feel to TWiki screens.Overview
TWiki uses TWikiTemplates files as the basis of all the screens it uses to interact with users. Each screen has an associated template file that contains the basic layout of the screen. This is then filled in by the code to generate what you see in the browser. TWiki ships with a default set of template files that give a very basic, CSS-themable, look-and-feel. TWiki also includes support for skins that can be selected to give different, more sophisticated, look and feel. A default TWiki installation will usually start up with the PatternSkin already selected. Skins may also be defined by third parties and loaded into a TWiki installation to give more options. To see how TWiki looks when no skin is selected, view the current page with a non-existing skin. TWiki topic content is not affected by the choice of skin, however a skin can be defined to use a CSS (Cascading Style Sheet) which can provide a radically different appearance to the text layout. Relevant links on TWiki.org:- TWiki:TWiki.TWikiSkinsSupplement
 -
-  tip: supplemental documentation on TWiki skins
tip: supplemental documentation on TWiki skins
- TWiki:Plugins.SkinPackage
 - list of all contributed skin packages
- list of all contributed skin packages
- TWiki:Plugins.SkinDevelopment
 - discussion and feedback on contributed skins
- discussion and feedback on contributed skins
- TWiki:Plugins.SkinBrainstorming
 - open forum for new skin ideas
- open forum for new skin ideas
- TWiki:Plugins.SkinPackageHowTo
 - template to create a new skin package
- template to create a new skin package
Changing the default TWiki skin
TWiki ships with the TopMenuSkin activated by default. You can set a skin for the whole site, a single web, a single topic, or for each user individually. This is done by setting the SKIN preferences setting to the name of a skin. If the skin you select doesn't exist, then TWiki will pick up the default templates. For example, to make the SKIN setting work across all topics and webs, put it in TWikiPreferences. Skins can cascade using a skin path explained below. One skin can be based on another one, and extensions can introduce additional screen elements. For example, the TagMePlugin adds tag elements to the TopMenuSkin, and the TopMenuSkin is based on the PatternSkin, resulting in this skin path:* Set SKIN = tagme, topmenu, pattern
Defining Skins
You may want to define your own skin, for example to comply with corporate web guidelines, or because you have a aesthetic vision that you want to share. There are a couple of places you can start doing this. The TWikiTemplates files used for skins are located in thetwiki/templates directory and are named according to the skin: <scriptname>.<skin>.tmpl. Skin files may also be defined in TWiki topics - see TWikiTemplates for details.
To start creating a new skin, copy the default TWikiTemplates (like view.tmpl), or copy an existing skin to use as a base for your own skin. You should only need to copy the files you intend to customize, as TWiki can be configured to fall back to another skin if a template is not defined in your skin. Name the files as described above (for example view.myskin.tmpl).
If you use PatternSkin as your starting point, and you want to modify the layout, colors or even the templates to suit your own needs, have a look first at the topics PatternSkinCustomization and PatternSkinCssCookbook.
For your own TWiki skin we encourage you to show a small TWiki logo at the bottom of your skin:
%WEBCOPYRIGHT% variable.
text skin, and skin names starting with rss have hard-coded meanings.
The following template files are used for TWiki screens, and are referenced in the TWiki core code. If a skin doesn't define its own version of a template file, then TWiki will fall back to the next skin in the skin path, or finally, to the default version of the template file.
(Certain template files are expected to provide certain TMPL:DEFs - these are listed in sub-bullets) -
addform- used to select a new form for a topic -
attachagain- used when refreshing an existing attachment -
attachnew- used when attaching a new file to a topic -
attachtables- defines the format of attachments at the bottom of the standard topic view-
ATTACH:files:footer,ATTACH:files:header,ATTACH:files:row,ATTACH:versions:footer,ATTACH:versions:header,ATTACH:versions:row
-
-
changeform- used to change the form in a topic -
changes- used by thechangesscript -
edit- used for the edit screen -
form -
formtables- used to defined the format of forms-
FORM:display:footer,FORM:display:header,FORM:display:row
-
-
login- used for loggin in when using the TemplateLoginManager-
LOG_IN,LOG_IN_BANNER,LOG_OUT,LOGGED_IN_BANNER,NEW_USER_NOTE,UNRECOGNISED_USER
-
-
moveattachment- used when moving an attachment -
oopsaccessdenied- used to format Access Denied messages-
no_such_topic,no_such_web,only_group,topic_access
-
-
oopsattention- used to format Attention messages-
already_exists,bad_email,bad_ver_code,bad_wikiname,base_web_missing,confirm,created_web,delete_err,invalid_web_color,invalid_web_name,in_a_group,mandatory_field,merge_notice,missing_action,missing_fields,move_err,missing_action,no_form_def,no_users_to_reset,notwikiuser,oversized_upload,password_changed,password_mismatch,problem_adding,remove_user_done,rename_err,rename_not_wikiword,rename_topic_exists,rename_web_err,rename_web_exists,rename_web_prerequisites,reset_bad,reset_ok,save_error,send_mail_error,thanks,topic_exists,unrecognized_action,upload_name_changed,web_creation_error,web_exists,web_missing,wrong_password,zero_size_upload
-
-
oopschangelanguage- used to prompt for a new language when internationalisation is enabled -
oopsgeneric- a basic dialog for user information; provides "ok" button only -
oopslanguagechanged- used to confirm a new language when internationalisation is enabled -
oopsleaseconflict- used to format lease Conflict messages-
lease_active,lease_old
-
-
preview- used for previewing edited topics before saving -
rdiff- used for viewing topic differences -
registernotify- used by the user registration system -
registernotifyadmin- used by the user registration system -
rename- used when renaming a topic -
renameconfirm- used when renaming a topic -
renamedelete- used when renaming a topic -
renameweb- used when renaming a web -
renamewebconfirm- used when renaming a web -
renamewebdelete- used when renaming a web -
searchbookview- used to format inline search results in book view -
searchformat- used to format inline search results -
search- used by thesearchCGI script -
settings -
view- used by theviewCGI script -
viewprint- used to create the printable view
twiki.tmpl is a master template conventionally used by other templates, but not used directly by code.
<p /> in the generated html. It will produce invalid html, and may break the page layout.
Partial customization, or adding in new features to an existing skin
You can use recursion in the TMPL:INCLUDE chain (e.g.twiki.pattern.tmpl contains %TMPL:INCLUDE{"twiki"}%, the templating system will include the next twiki.SKIN in the skin path (which is explained below). For example, to create a customization of pattern skin, where you only want to remove the edit & WYSIWYG buttons from view page, you create only a view.yourlocal.tmpl:
%TMPL:INCLUDE{"view"}%
%TMPL:DEF{"edit_topic_link"}%%TMPL:END%
%TMPL:DEF{"edit_wysiwyg_link"}%%TMPL:END%
and then set SKIN=yourlocal,pattern.
Variables in Skins
You can use template variables, TWikiVariables, and other predefined variables to compose your skins. Some commonly used variables in skins:| Variable: | Expanded to: |
|---|---|
%WEBLOGONAME% |
Filename of web logo |
%WEBLOGOIMG% |
Image URL of web logo |
%WEBLOGOURL% |
Link of web logo |
%WEBLOGOALT% |
Alt text of web logo |
%WIKILOGOURL% |
Link of page logo |
%WIKILOGOIMG% |
Image URL of page logo |
%WIKILOGOALT% |
Alt text of page logo |
%WEBBGCOLOR% |
Web-specific background color, defined in the WebPreferences |
%WIKITOOLNAME% |
The name of your TWiki site |
%SCRIPTURL% |
The script URL of TWiki |
%SCRIPTURLPATH% |
The script URL path |
%SCRIPTSUFFIX% |
The script suffix, ex: .pl, .cgi |
%WEB% |
The name of the current web. |
%TOPIC% |
The name of the current topic. |
%WEBTOPICLIST% |
Common links of current web, defined in the WebPreferences. It includes a Jump box |
%TEXT% |
The topic text, e.g. the content that can be edited |
%META{"form"}% |
TWikiForm, if any |
%META{"attachments"}% |
FileAttachment table |
%META{"parent"}% |
The topic parent |
%EDITTOPIC% |
Edit link |
%REVTITLE% |
The revision title, if any, ex: (r1.6) |
%REVINFO% |
Revision info, ex: r1.6 - 24 Dec 2002 - 08:12 GMT - TWikiGuest |
%WEBCOPYRIGHT% |
Copyright notice, defined in the WebPreferences |
%BROADCASTMESSAGE% |
Broadcast message at the beginning of your view template, can be used to alert users of scheduled downtimes; can be set in TWikiPreferences |
The Jump Box and Navigation Box
The default skins include a Jump Box, to jump to a topic. The box also understands URLs, e.g. you can typehttp://www.google.com/ to jump to an external web site. The feature is handy if you build a skin that has a select box of frequently used links, like Intranet home, employee database, sales database and such. A little JavaScript gets into action on the onchange method of the select tag to fill the selected URL into the "Go" box field, then submits the form.
Here is an example form that has a select box and the Jump Box for illustration purposes. You need to have JavaScript enabled for this to work:
Note: Redirect to a URL only works if it is enabled in configure (Miscellaneous, {AllowRedirectUrl}).
Using Cascading Style Sheets
CSS files are gererally attachments to the skin topic that are included in the the skin templates - in the case of PatternSkin in the templatestyles.pattern.tmpl.
- To see how CSS is used in the default TWiki skin, see: PatternSkin
- If you write a complete new skin, this is the syntax to use in a template file:
<style type='text/css' media='all'>@import url('%PUBURLPATH%/%SYSTEMWEB%/MySkin/mystyle.css');</style>
Attachment Tables
Controlling the look and feel of attachment tables is a little bit more complex than for the rest of a skin. By default, the attachment table is a standard TWiki table, and the look is controlled in the same way as other tables. In a very few cases you may want to change the content of the table as well. The format of standard attachment tables is defined through the use of special TWiki template macros which by default, are defined in theattachtables.tmpl template using the %TMPL:DEF macro syntax described in TWikiTemplates. These macros are:
| Macro | Description |
|---|---|
ATTACH:files:header |
Standard title bar |
ATTACH:files:row |
Standard row |
ATTACH:files:footer |
Footer for all screens |
ATTACH:files:header:A |
Title bar for upload screens, with attributes column |
ATTACH:files:row:A |
Row for upload screen |
ATTACH:files:footer:A |
Footer for all screens |
| Macro | Description |
|---|---|
ATTACH:versions:header |
Header for versions table on upload screen |
ATTACH:versions:row |
Row format for versions table on upload screen |
ATTACH:versions:footer |
Footer for versions table on upload screen |
ATTACH:row macros are expanded for each file in the attachment table, using the following special tags:
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
%A_URL% |
viewfile URL that will recover the file |
%A_REV% |
Revision of this file |
%A_ICON% |
A file icon suitable for representing the attachment content |
%A_FILE% |
The name of the file. To get the 'pub' url of the file, use %PUBURL%/%WEB%/%TOPIC%/%A_FILE% |
%A_SIZE% |
The size of the file |
%A_DATE% |
The date the file was uploaded |
%A_USER% |
The user who uploaded it |
%A_COMMENT% |
The comment they put in when uploading it |
%A_ATTRS% |
The attributes of the file as seen on the upload screen e.g "h" for a hidden file |
Packaging and Publishing Skins
See TWiki:Plugins/SkinPackagingHowToBrowsing Installed Skins
You can try out all installed skins in the TWikiSkinBrowser.Activating Skins
TWiki uses a skin search path, which lets you combine skins additively. The skin path is defined using a combination of TWikiVariables and URL parameters. TWiki works by asking for a template for a particular function - for example, 'view'. The detail of how templates are searched for is described in TWikiTemplates, but in summary, the templates directory is searched for a file calledview.skin.tmpl, where skin is the name of the skin e.g. pattern. If no template is found, then the fallback is to use view.tmpl. Each skin on the path is searched for in turn. For example, if you have set the skin path to local,pattern then view.local.tmpl will be searched for first, then view.pattern.tmpl and finally view.tmpl.
The basic skin is defined by a SKIN setting:
-
Set SKIN = catskin, bearskin
?skin=catskin,bearskin:
Setting SKIN (or the ?skin parameter in the URL) replaces the existing skin path setting, for the current page only. You can also extend the existing skin path as well, using covers.
-
Set COVER = ruskin
ruskin, catskin, bearskin). There is also an equivalent cover URL parameter. The difference between setting SKIN vs. COVER is that if the chosen template is not found (e.g., for included templates), SKIN will fall back onto the next skin in line, or the default skin, if only one skin was present, while COVER will always fall back onto the current skin.
An example would be invoking the printable mode, which is achieved by applying ?cover=print. The view.print.tmpl simply invokes the viewprint template for the current skin which then can appropriately include all other used templates for the current skin. Where the printable mode be applied by using SKIN, all skins would have the same printable appearance.
The full skin path is built up as follows: SKIN setting (or ?skin if it is set), then COVER setting is added, then ?cover.
Conditional Skin Activation
TWiki skins can be activated conditionally using IfStatements. For example, you might want to use a mobile skin for iPhone and Android user agents, and the default skin otherwise. This example uses the print skin on iPhone and Android:
* Set SKIN = %IF{
"'%HTTP{"User-Agent"}%'~'*iPhone*' OR '%HTTP{"User-Agent"}%'~'*Android*'"
then="print, pattern"
else="topmenu, pattern"
}%
Hard-Coded Skins
Thetext skin is reserved for TWiki internal use.
Skin names starting with rss also have a special meaning; if one or more of the skins in the skin path starts with 'rss' then 8-bit characters will be encoded as XML entities in the output, and the content-type header will be forced to text/xml.
Related Topics: TWikiSkinBrowser, AdminDocumentationCategory, DeveloperDocumentationCategory, TWiki:TWiki.TWikiSkinsSupplementTWiki Variables
Special text strings expand on the fly to display dynamic content, such as user data or system info TWikiVariables are text strings -%VARIABLE% or %VARIABLE{ parameter="value" }% - that expand into content whenever a topic is rendered for viewing. There are two types of variables:
- Preferences variables: Can be defined and changed by the user.
Example:%T%renders as
- Predefined variables: Defined by the TWiki system or by extensions.
Example:%CALCULATE{}%is handled by the SpreadSheetPlugin
TWiki Variables Wizard
|
Categories:
|
Variables:
|
Select a category and a variable
Build Your Variable:
Using Variables
To use a variable type its name. For example,- type
%T%to get (a preferences variable)
(a preferences variable)
- type
%TOPIC%to getTWikiVariables(a predefined variable) - type
%CALCULATE{ "$UPPER(Text)" }%to getTEXT(a variable defined by a plugin)
- To leave a variable unexpanded, precede it with an exclamation point, e.g. type
!%TOPIC%to get%TOPIC% - Variables are expanded relative to the topic they are used in, not the topic they are defined in
- Type
%ALLVARIABLES%to get a full listing of all variables defined for a particular topic
Variable Names
Variable names must start with a letter, optionally followed by letters, numbers and underscore '_' characters. Both upper-case and lower-case characters can be used,%MYVAR%, %MyVar%, %My2ndVar%, and %My_Var% are valid names. Variables are case sensitive, e.g. %MyVAR% and %MYVAR% are not the same.
By convention all settings, predefined variables and variables handled by extensions are always UPPER-CASE.
Preferences Variables
Unlike predefined variables, preferences variables can be defined by the user in various places.Setting Preferences Variables
You can set variables in all the following places:- system level in TWiki.TWikiPreferences
- plugin topics (see TWikiPlugins)
- local site level in Main.TWikiPreferences
- user level in individual user topics in Main web
- If UserSubwebs is in effect, the topic specified by
%USERPREFSTOPIC%in the user's subweb is read instead - If
$TWiki::cfg{DemoteUserPreferences}is true, this step is deferred to a later step. On this TWiki installation,$TWiki::cfg{DemoteUserPreferences}is false
- If UserSubwebs is in effect, the topic specified by
- web level in WebPreferences of each web
- If
EXTRAPREFERENCESis defined at this point, it's regarded as having comma separated list of topics. Those topics are read in the listed order as if they were WebPreferences - topic level in topics in webs
- session variables (if sessions are enabled)
- user level preferences are set at this point if
$TWiki::cfg{DemoteUserPreferences}is true as mentioned at the step 4
preview will show the wrong thing, and you must save the topic to see it correctly.
The syntax for setting variables is the same anywhere in TWiki (on its own TWiki bullet line, including nested bullets): [multiple of 3 spaces] * [space] Set [space] VARIABLENAME [space] = [space] value
Examples:
* Set VARIABLENAME1 = value
* Set VARIABLENAME2 = value
Spaces between the = sign and the value will be ignored. You can split a value over several lines by indenting following lines with spaces - as long as you don't try to use * as the first character on the following line.
Example:
* Set VARIABLENAME = value starts here
and continues here
Whatever you include in your variable will be expanded on display, exactly as if it had been entered directly.
Example: Create a custom logo variable - To place a logo anywhere in a web by typing
%MYLOGO%, define the Variable on the web's WebPreferences topic, and upload a logo file, ex:mylogo.gif. You can upload by attaching the file to WebPreferences, or, to avoid clutter, to any other topic in the same web, e.g.LogoTopic. Sample variable setting in WebPreferences:
* Set MYLOGO = %PUBURL%/%WEB%/LogoTopic/mylogo.gif
You can also set preferences variables on a topic by clicking the link Edit topic preference settings under More topic actions. Use the same * Set VARIABLENAME = value syntax. Preferences set in this manner are not visible in the topic text, but take effect nevertheless.
Controlling User Level Preferences Override
By default, user level variables are set at the step 4 as stated in the previous section. That means a user can finalise some preferences variables so that web level or topic level setting cannot override it. This may result in a situation the web or page owner doesn't expect.$TWiki::cfg{DemoteUserPreferences} has been introduced to avoid it.
If it's set to true, user level variables are set at the last step instead of the step 4.
But this is not enough.
To guarantee a certain result, you need to finalise critical preferences variables set at the web or topic level, which is cumbersome.
So preferences variables DENYUSERPREFEENCES and ALLOWUSERPREFEENCES have been introduced. -
DENYUSERPREFEENCESandALLOWUSERPREFEENCESmay have comma separated list of variable names - If a preferences variable is listed in
DENYUSERPREFEENCES, the variable cannot be overridden at the user level. There is a special value "all", which means no preferences variables can be overridden at the user level - If
ALLOWUSERPREFEENCESis set and not empty, only the listed preferences variables can be overridden. There is a special value "all", which means any preferences variable can be overridden at the user level. But actually, "all" is not necessary since a blank value or not settingALLOWUSERPREFEENCEShas the same effect -
DENYUSERPREFEENCEStakes precedence overALLOWUSERPREFEENCES. If a variable is listed on both, it cannot be overridden. IfDENYUSERPREFEENCESis "all", the value ofALLOWUSERPREFEENCESdoesn't matter.
* Set DENYUSERPREFERENCES = allIf you allow
INYMCEPLUGIN_DISABLE and SKIN to be set at the user level:
* Set ALLOWUSERPREFERENCES = TINYMCEPLUGIN_DISABLE, SKINIf you allow user preferences to set anything other than
TINYMCEPLUGIN_DISABLE or SKIN:
* Set DENYUSERPREFERENCES = TINYMCEPLUGIN_DISABLE, SKINPlease note
DENYUSERPREFEENCES and ALLOWUSERPREFEENCES affect user preferences regardless of $TWiki::cfg{DemoteUserPreferences}.
You can set those variables at the site level while $TWiki::cfg{DemoteUserPreferences} setting to false.
If you do so, you should finalise DENYUSERPREFEENCES and ALLOWUSERPREFEENCES.
Otherwise, they might be overridden by user preferences.
You will get the most benefit of DENYUSERPREFEENCES and ALLOWUSERPREFEENCES by setting $TWiki::cfg{DemoteUserPreferences} to true.
That way, each web can specify how much user level preferences overriding is allowed.
Parameterized Variables (Macros)
It is possible to pass parameters to TWiki variables. This is called a macro in a programming language. To define a parameterized variable, set a variable that contains other variables, such as:
* Set EXAMPLE = Example variable using %DEFAULT%, %PARAM1% and %PARAM2%
* Set DEMO = Demo using %DEFAULT{ default="(undefined)" }%,
%PARAM1{ default="(undefined)" }% and %PARAM2{ default="(undefined)" }%
A special %DEFAULT% variable denotes the default (nameless) parameter of the calling variable. Variables optionally may list a default="..." parameter that gets used in case the calling variable does not specify that parameter.
To use a parameterized variable (or call a macro), add parameters within the curly brackets, such as:
* %EXAMPLE{ "foo" PARAM1="bar" PARAM2="baz" }%
* %DEMO{ "demo" PARAM2="parameter 2" }% -- note that PARAM1 is missing
which resolves to: - %EXAMPLE{ "foo" PARAM1="bar" PARAM2="baz" }%
- %DEMO{ "demo" PARAM2="parameter 2" }% -- note that PARAM1 is missing
- Parameter from variable call. In above example,
%PARAM1%gets expanded tobar. - Session variable and preferences settings
Example
Define variables:
* Set DRINK = red wine
* Set FAVORITE = My %DEFAULT{default="favorite"}% dish is %DISH{default="steak"}%,
my %DEFAULT{default="favorite"}% drink is %DRINK%.
%DISH{default="steak"}%), or as a preferences setting (Set DRINK = ...).
Use Variables:
%FAVORITE{ DISH="Sushi" DRINK="Sake" }%
Returns: %FAVORITE{ DISH="Sushi" DRINK="Sake" }%
%FAVORITE{}%
Returns: %FAVORITE{}%
%FAVORITE{ "preferred" }%
Returns: %FAVORITE{ "preferred" }%
Access Control Variables
These are special types of preferences variables to control access to content. TWikiAccessControl explains these security settings in detail.Local values for variables
Certain topics (a users home topic, web site and default preferences topics) have a problem; variables defined in those topics can have two meanings. For example, consider a user topic. A user may want to use a double-height edit box when they are editing their home topic - but only when editing their home topic. The rest of the time, they want to have a normal edit box. This separation is achieved usingLocal in place of Set in the variable definition. For example, if the user sets the following in their home topic:
* Set EDITBOXHEIGHT = 10 * Local EDITBOXHEIGHT = 20Then when they are editing any other topic, they will get a 10 high edit box. However when they are editing their home topic, they will get a 20 high edit box.
Local can be used wherever a preference needs to take a different value depending on where the current operation is being performed.
Use this powerful feature with great care! %ALLVARIABLES% can be used to get a listing of the values of all variables in their evaluation order, so you can see variable scope if you get confused.
Frequently Used Preferences Variables
The following preferences variables are frequently used. They are defined in TWikiPreferences#Miscellaneous_Settings:-
%BB%- line break and bullet combined -
%BB2%- level 2 bullet with line break -
%BB3%- level 3 bullet with line break -
%BB4%- level 4 bullet with line break -
%BR%- line break -
%BULLET%- bullet sign -
%CARET%- caret symbol -
%VBAR%- vertical bar -
%H%- Help icon
Help icon
-
%I%- Idea icon
Idea icon
-
%M%- Moved to icon
Moved to icon
-
%N%- New icon
New icon
-
%P%- Refactor icon
Refactor icon
-
%Q%- Question icon
Question icon
-
%S%- Pick icon
Pick icon
-
%T%- Tip icon
Tip icon
-
%U%- Updated icon
Updated icon
-
%X%- Alert icon
Alert icon
-
%Y%- Done icon
Done icon
-
%RED% text %ENDCOLOR%- colored text (also%YELLOW%,%ORANGE%,%PINK%,%PURPLE%,%TEAL%,%NAVY%,%BLUE%,%AQUA%,%LIME%,%GREEN%,%OLIVE%,%MAROON%,%BROWN%,%BLACK%,%GRAY%,%SILVER%,%WHITE%) -
%REDBG% text %ENDBG%- colored background (also%YELLOWBG%,%ORANGEBG%,%PINKBG%,%PURPLEBG%,%TEALBG%,%NAVYBG%,%BLUEBG%,%AQUABG%,%LIMEBG%,%GREENBG%,%OLIVEBG%,%MAROONBG%,%BROWNBG%,%BLACKBG%,%GRAYBG%,%SILVERBG%,%WHITEBG%)
Predefined Variables
Most predefined variables return values that were either set in the configuration when TWiki was installed, or taken from server info (such as current username, or date and time). Some, like%SEARCH%, are powerful and general tools.
- Show all TWiki Variables
- Predefined variables can be overridden by preferences variables (except a few such as TOPIC and WEB)
- This has long been the case but may not be desirable since even something as fundamental as
%IF{...}%,%SCRIPT{...}%, and%INCLUDE{...}%can be overridden - So TWiki-6.0.1 has introduced a way to protect predefined variables from being overridden by preferences variables
- The preferences variable
OVERRIDABLEPREDEFINEDVARIABLEShaving a comma separated list of predefined variables specifies which predefined variables are overridable - By default, it's set to "all" (set at TWiki.TWikiPreferences), which means any predefined variable can be overridden, which is for compatibility with prior releases. You can set it to a different value in Main.TWikiPreferences and you may finalise it
- If it's set as below, all predefined variables are protected
*
Set OVERRIDABLEPREDEFINEDVARIABLES = - If it's set as below,
DATEandLANGUAGEpredefined variables can be overridden but all the other predefined variables cannot*
Set OVERRIDABLEPREDEFINEDVARIABLES = DATE, LANGUAGE
- This has long been the case but may not be desirable since even something as fundamental as
- Extensions may extend the set of predefined variables (see individual extension topics for details)
- Take the time to thoroughly read through ALL preference variables. If you actively configure your site, review variables periodically. They cover a wide range of functions, and it can be easy to miss the one perfect variable for something you have in mind. For example, see
%INCLUDINGTOPIC%,%INCLUDE%, and the mighty%SEARCH%.
Search or List Variables by Category
Documenting TWiki Variables
This section is for people documenting TWiki variables of the TWiki core and TWiki extensions. Each variable is documented in a topic namedVar<name> in the TWiki web. For example, a %LIGHTSABER% variable has a documentation topic called VarLIGHTSABER. The topic is expected to have a specific format so that reports in this TWikiVariables topic, in TWikiVariablesSearch and in category topics work as expected.
Basic structure of a variable documentation topic:
- Parent set to TWikiVariables
- An anchor named the same like the topic, such as
#VarLIGHTSABER - A
---+++(level 3) heading with variable name,--, short description - A bullet with description of the variable (optional)
- A
Syntax:bullet with example syntax - A
Parameters:bullet with a table explaining the parameters (optional) - An
Example:bullet or two with examples - An
Expands to:bullet with expanded variable (optional) - A
Note:bullet with notes (optional) - A
Category:bullet with one or more of the TWiki variables categories:
AdministrationVariables, ApplicationsAndComponentsVariables, AttachmentsAndFilesVariables, ChartingAndDrawingVariables, DatabaseAndFormsVariables, DateAndTimeVariables, DevelopmentVariables, EditingAndContentUpdateVariables, EmailAndNotificationVariables, ExportAndPublishingVariables, FormattingAndRenderingVariables, ImportVariables, LinkingAndNavigationVariables, SearchingAndListingVariables, SecurityAndAccessControlVariables, SkinsAndTemplatesVariables, SystemInformationVariables, TablesAndSpreadsheetsVariables, UIAndVisualizationVariables, UsersAndAuthenticationVariables, WorkflowAndAutomationVariables - A
Related:bullet with related links. Links have conditional IF so that links work properly locally in variable documentation topics and in the TWikiVariables topic
VarLIGHTSABER topic:
#VarLIGHTSABER
---+++ LIGHTSABER -- laser sword to fend of unethical competition
* The =%<nop>LIGHTSABER{}%= variable is handled by the LightsaberPlugin.
* Syntax: =%<nop>LIGHTSABER{ _parameters_ }%=
* Parameters:
| *Parameter* | *Description* | *Default* |
| =color="..."= | Color: =red=, =glue=, =green= | =white= |
| =sound="..."= | Sound: =none=, =standard=, =loud= | =none= |
* Example: =%<nop>LIGHTSABER{ color="red" }%= shows a red Lightsaber
* Expands to: =%LIGHTSABER{ color="red" }%=
* Note: The Lightsaber is a fictional weapon in the Star Wars universe, a "laser sword."
* Category: FormattingAndRenderingVariables, UIAndVisualizationVariables
* Related: [[%IF{"'%INCLUDINGTOPIC%'='TWikiVariables'" then="#"}%VarPLASMA][PLASMA]], LightsaberPlugin
TWiki Meta Data
Additional topic data, program-generated or from TWikiForms, is stored embedded in the topic text usingMETA: tags
Overview
By default, TWiki stores topics in files on disk, in a really simple and obvious directory structure. The big advantage of this approach is that it makes it really easy to manipulate topics from outside TWiki, and is also very safe; there are no complex binary indexes to maintain, and moving a topic from one TWiki to another is as simple as copying a couple of text files. To keep everything together in one place, TWiki uses a simple method for embedding additional data (program-generated or from TWikiForms) in topics. It does this usingMETA: tags.
META: data includes program-generated info like FileAttachment and topic movement data, and user-defined TWikiForms info.
Meta Data Syntax
- Format is the same as in TWikiVariables, except all fields have a key.
-
%META:<type>{key1="value1" key2="value2" ...}%
-
- Order of fields within the meta variables is not defined, except that if there is a field with key
name, this appears first for easier searching (note the order of the variables themselves is defined).
- Each meta variable is on one line.
- Values in meta-data are URL encoded so that characters such as \n can be stored.
Example of Format
%META:TOPICINFO{version="1.6" date="976762663" author="LastEditorWikiName" format="1.0"}%
text of the topic
%META:TOPICMOVED{from="Codev.OldName" to="Codev.NewName"
by="TopicMoverWikiName" date="976762680"}%
%META:TOPICPARENT{name="NavigationByTopicContext"}%
%META:FILEATTACHMENT{name="Sample.txt" version="1.3" ... }%
%META:FILEATTACHMENT{name="Smile.gif" version="1.1" ... }%
%META:FORM{name="WebFormTemplate"}%
%META:FIELD{name="OperatingSystem" value="OsWin"}%
%META:FIELD{name="TopicClassification" value="PublicFAQ"}%
Meta Data Specifications
The current version of Meta Data is 1.0, with support for the following variables.META:TOPICINFO
| Key | Comment |
|---|---|
| version | Same as RCS version |
| date | integer, unix time, seconds since start 1970 |
| author | last to change topic, is the REMOTE_USER |
| format | Format of this topic, will be used for automatic format conversion |
META:TOPICMOVED
This is optional, exists if topic has ever been moved. If a topic is moved more than once, only the most recent META:TOPICMOVED meta variable exists in the topic, older ones are to be found in the rcs history.%META:TOPICMOVED{from="Codev.OldName" to="Codev.NewName" by="talintj" date="976762680"}%
| Key | Comment |
|---|---|
| from | Full name, i.e., web.topic |
| to | Full name, i.e., web.topic |
| by | Who did it, is the REMOTE_USER, not WikiName |
| date | integer, unix time, seconds since start 1970 |
- at present version number is not supported directly, it can be inferred from the RCS history.
- there is only one META:TOPICMOVED in a topic, older move information can be found in the RCS history.
META:TOPICPARENT
| Key | Comment |
|---|---|
| name | The topic from which this was created, typically when clicking on a red-link, or by filling out a form. Normally just TopicName, but it can be a full Web.TopicName format if the parent is in a different Web. |
META:FILEATTACHMENT
| Key | Comment |
|---|---|
| name | Name of file, no path. Must be unique within topic |
| version | Same as RCS revision |
| path | Full path file was loaded from |
| size | In bytes |
| date | integer, unix time, seconds since start 1970 |
| user | the REMOTE_USER, not WikiName |
| comment | As supplied when file uploaded |
| attr | h if hidden, optional |
| Key | Comment |
|---|---|
| movedfrom | full topic name - web.topic |
| movedby | the REMOTE_USER, not WikiName |
| movedto | full topic name - web.topic |
| moveddate | integer, unix time, seconds since start 1970 |
META:FORM
| Key | Comment |
|---|---|
| name | A topic name - the topic represents one of the TWikiForms. Can optionally include the web name (i.e., web.topic), but doesn't normally |
META:FIELD
Should only be present if there is a META:FORM entry. Note that this data is used when viewing a topic, the form template definition is not read.| Key | Name |
|---|---|
| name | Ties to entry in TWikiForms template, is title with all bar alphanumerics and . removed |
| title | Full text from TWikiForms template |
| value | Value user has supplied via form |
Recommended Sequence
There is no absolute need for Meta Data variables to be listed in a specific order within a topic, but it makes sense to do so a couple of good reasons:- form fields remain in the order they are defined
- the
difffunction output appears in a logical order
-
META:TOPICINFO -
META:TOPICPARENT(optional) - text of topic
-
META:TOPICMOVED(optional) -
META:FILEATTACHMENT(0 or more entries) -
META:FORM(optional) -
META:FIELD(0 or more entries; FORM required)
Viewing Meta Data in Page Source
When viewing a topic theRaw Text link can be clicked to show the text of a topic (i.e., as seen when editing). This is done by adding raw=on to URL. raw=debug shows the meta data as well as the topic data, ex: debug view for this topic
Rendering Meta Data
Meta Data is rendered with the %META% variable. This is mostly used in theview, preview and edit scripts.
You can render form fields in topic text by using the FORMFIELD variable. Example:%FORMFIELD{"TopicClassification"}% For details, see VarFORMFIELD. Current support covers:
| Variable usage: | Comment: |
|---|---|
%META{"form"}% |
Show form data, see TWikiForms. |
%META{"formfield"}% |
Show form field value. Parameter: name="field_name". Example:%META{ "formfield" name="TopicClassification" }% |
%META{"attachments"}% |
Show attachments, except for hidden ones. Options: all="on": Show all attachments, including hidden ones. |
%META{"moved"}% |
Details of any topic moves. |
%META{"parent"}% |
Show topic parent. Options: dontrecurse="on": By default recurses up tree, at some cost. nowebhome="on": Suppress WebHome. prefix="...": Prefix for parents, only if there are parents, default "". suffix="...": Suffix, only appears if there are parents, default "". separator="...": Separator between parents, default is " > ". |
Warning: Can't find topic TWiki.TWikiFormTemplate
TWiki Plugins
Add functionality to TWiki with readily available plugins; create plugins based on APIsOverview
You can add plugins to extend TWiki functionality, without altering the core code. A plug-in approach lets you:- add virtually unlimited features while keeping the main TWiki code compact and efficient;
- heavily customize an installation and still do clean updates to new versions of TWiki;
- rapidly develop new TWiki functions in Perl using the plugin API.
- TWiki:TWiki.TWikiPluginsSupplement
 -
-  tip: supplemental documentation on TWiki plugins
tip: supplemental documentation on TWiki plugins
- TWiki:Plugins.PluginPackage
 - list of all contributed plugin packages
- list of all contributed plugin packages
- TWiki:Plugins.PluginDevelopment
 - discussion and feedback on contributed plugins
- discussion and feedback on contributed plugins
- TWiki:Plugins.PluginBrainstorming
 - open forum for new plugin ideas
- open forum for new plugin ideas
- TWiki:Plugins.PluginPackageHowTo
 - template to create a new plugin package
- template to create a new plugin package
Installing Plugins
The TWiki:Pluginsyum, apt-get, rpm, etc) to install dependent libraries.
If available, install CPAN (Comprehensive Perl Archive Network) libraries with the OS package manager. For example, to install IO::Socket::SSL on Fedora/RedHat/CentOS, run yum install perl-IO-Socket-SSL. CPAN modules can also be installed natively, see TWiki:TWiki.HowToInstallCpanModulesOn-Site Pretesting
If you have a mission critical TWiki installation and you are concerned about installing new plugins, you can test new plugins before making them available by creating a second test TWiki installation, and test the plugin there. It is also possible to configure this test TWiki to use the live data. You can allow selected users access to the test area. Once you are satisfied that it won't compromise your primary installation, you can install it there as well. InstalledPlugins shows which plugins are: 1) installed, 2) loading properly, and 3) what TWiki:Codev.PluginHandlers%FAILEDPLUGINS% variable can be used to debug failures. You may also want to check your webserver error log and the various TWiki log files.
Some Notes on Plugin Performance
The performance of the system depends to some extent on the number of plugins installed and on the plugin implementation. Some plugins impose no measurable performance decrease, some do. For example, a Plugin might use many Perl libraries that need to be initialized with each page view (unless you run mod_perl). You can only really tell the performance impact by installing the plugin and by measuring the performance with and without the new plugin. Use the TWiki:Plugins.PluginBenchmarkAddOnab utility. Example on Unix:time wget -qO /dev/null /bin/view/TWiki/AbcPlugin
DISABLEDPLUGINS to be a comma-separated list of names of plugins to disable. Define it in Main.TWikiPreferences to disable those plugins everywhere, in the WebPreferences topic to disable them in an individual web, or in a topic to disable them in that topic. For example,
* Set DISABLEDPLUGINS = SpreadSheetPlugin, EditTablePlugin
Managing Installed Plugins
Some plugins require additional settings or offer extra options that you have to select. Also, you may want to make a plugin available only in certain webs, or temporarily disable it. And may want to list all available plugins in certain topics. You can handle all of these management tasks with simple procedures:Enabling/Disabling Plugins
Plugins can be enabled and disabled with the configure script in the Plugins section. An installed plugin needs to be enabled before it can be used.Plugin Evaluation Order
By default, TWiki executes plugins in alphabetical order on plugin name. It is possible to change the order, for example to evaluate database variables before the spreadsheet CALCs. This can be done with{PluginsOrder} in the plugins section of configure.
Plugin-Specific Settings
Plugins can be configured with 1. preferences settings and/or 2. with configure settings. Older plugins use plugin preferences settings defined in the plugin topic, which is no longer recommended. 1. Use preferences settings: Adinistrators can set plugin-specific settings in the local site preferences at Main.TWikiPreferences and users can overload them at the web level and page level. This approach is recommended if users should be able to overload settings. For security this is not recommended for system settings, such as a path to an executable. By convention, preferences setting names start with the plugin name in all caps, and an underscore. For example, to set the cache refresh period of the TWiki:Plugins.VarCachePlugin-
Set VARCACHEPLUGIN_REFRESH = 24
%<pluginname>_<setting>%, such as %VARCACHEPLUGIN_REFRESH%.
To learn how this is done, use the TWiki:Plugins.VarCachePlugin- Create a Config.spec file in
lib/TWiki/Plugins/YourPlugin/with variables, such as
$TWiki::cfg{Plugins}{RecentVisitorPlugin}{ShowIP} = 0; - In the plugin, use those those variables, such as
$showIP = $TWiki::cfg{Plugins}{RecentVisitorPlugin}{ShowIP} || 0;
- As a setting in the plugin documentation, which is needed for the extension reports on twiki.org. Example:
-
Set SHORTDESCRIPTION = Show recent visitors to a TWiki site
-
- As a global Perl package variable in the plugin package, which is needed by TWiki to show info on installed plugins. Example:
our $SHORTDESCRIPTION = 'Show recent visitors to a TWiki site';
our $NO_PREFS_IN_TOPIC = 1;
Listing Active Plugins
Plugin status variables let you list all active plugins wherever needed. This site is running TWiki version TWiki-6.0.1, Sun, 05 Oct 2014, build 28207, plugin API version 6.01 %ACTIVATEDPLUGINS%
On this TWiki site, the enabled plugins are: SpreadSheetPlugin, BackupRestorePlugin, ColorPickerPlugin, CommentPlugin, DatePickerPlugin, EditTablePlugin, HeadlinesPlugin, InterwikiPlugin, JQueryPlugin, PreferencesPlugin, SetGetPlugin, SlideShowPlugin, SmiliesPlugin, TablePlugin, TagMePlugin, TinyMCEPlugin, TwistyPlugin, WatchlistPlugin, WysiwygPlugin.
%PLUGINDESCRIPTIONS%
- SpreadSheetPlugin (2014-09-23, $Rev: 28087 (2014-10-05) $): Add spreadsheet calculation like
"$SUM( $ABOVE() )"to TWiki tables or anywhere in topic text - BackupRestorePlugin (2013-02-16, $Rev: 25103 (2013-02-16) $): Administrator utility to backup, restore and upgrade a TWiki site
- ColorPickerPlugin (2013-02-15, $Rev: 26769 (2014-10-05) $): Color picker, packaged for use in TWiki forms and TWiki applications
- CommentPlugin (2013-02-10, $Rev: 26771 (2014-10-05) $): Quickly post comments to a page without an edit/preview/save cycle
- DatePickerPlugin (2013-09-04, $Rev: 26773 (2014-10-05) $): Pop-up calendar with date picker, for use in TWiki forms, HTML forms and TWiki plugins
- EditTablePlugin (2013-12-03, $Rev: 26775 (2014-10-05) $): Edit TWiki tables using edit fields, date pickers and drop down boxes
- HeadlinesPlugin (2013-11-18, $Rev: 26779 (2014-10-05) $): Show headline news in TWiki pages based on RSS and ATOM news feeds from external sites
- InterwikiPlugin (2014-10-03, $Rev: 28176 (2014-10-05) $): Write
ExternalSite:Pageto link to a page on an external site based on aliases defined in a rules topic - JQueryPlugin (2014-09-03, $Rev: 28041 (2014-10-05) $): jQuery JavaScript library for TWiki
- PreferencesPlugin (2014-05-30, $Rev: 27577 (2014-10-05) $): Allows editing of preferences using fields predefined in a form
- SetGetPlugin (2013-01-28, $Rev: 26789 (2014-10-05) $): Set and get variables in topics, optionally persistently across topic views
- SlideShowPlugin (2013-04-07, $Rev: 26791 (2014-10-05) $): Create web based presentations based on topics with headings.
- SmiliesPlugin (2013-01-13, $Rev: 26793 (2014-10-05) $): Render smilies as icons, like
:-)as or
or :eek:as
- TablePlugin (2014-01-21, $Rev: 26935 (2014-10-05) $): Control attributes of tables and sorting of table columns
- TagMePlugin (2014-05-15, $Rev: 27386 (2014-10-05) $): Tag wiki content collectively or authoritatively to find content by keywords
- TinyMCEPlugin (2013-09-18, $Rev: 26799 (2014-10-05) $): Integration of the Tiny MCE WYSIWYG Editor
- TwistyPlugin (2013-03-22, $Rev: 26803 (2014-10-05) $): Twisty section JavaScript library to open/close content dynamically
- WatchlistPlugin (2014-05-20, $Rev: 27429 (2014-10-05) $): Watch topics of interest and get notified of changes by e-mail
- WysiwygPlugin (2013-09-18, $Rev: 27021 (2014-10-05) $): Translator framework for WYSIWYG editors
%FAILEDPLUGINS%
| Plugin | Errors |
|---|---|
| SpreadSheetPlugin | none |
| BackupRestorePlugin | none |
| ColorPickerPlugin | none |
| CommentPlugin | none |
| DatePickerPlugin | none |
| EditTablePlugin | none |
| HeadlinesPlugin | none |
| InterwikiPlugin | none |
| JQueryPlugin | none |
| PreferencesPlugin | none |
| SetGetPlugin | none |
| SlideShowPlugin | none |
| SmiliesPlugin | none |
| TablePlugin | none |
| TagMePlugin | none |
| TinyMCEPlugin | none |
| TwistyPlugin | none |
| WatchlistPlugin | none |
| WysiwygPlugin | none |
| Handler | Plugins |
|---|---|
| afterEditHandler | WysiwygPlugin |
| afterRenameHandler | TagMePlugin WatchlistPlugin |
| afterSaveHandler | TagMePlugin WatchlistPlugin |
| beforeCommonTagsHandler | EditTablePlugin PreferencesPlugin TwistyPlugin WysiwygPlugin |
| beforeEditHandler | TinyMCEPlugin WysiwygPlugin |
| beforeMergeHandler | WysiwygPlugin |
| beforeSaveHandler | CommentPlugin WatchlistPlugin WysiwygPlugin |
| commonTagsHandler | SpreadSheetPlugin BackupRestorePlugin CommentPlugin EditTablePlugin JQueryPlugin SlideShowPlugin SmiliesPlugin |
| initPlugin | SpreadSheetPlugin BackupRestorePlugin ColorPickerPlugin CommentPlugin DatePickerPlugin EditTablePlugin HeadlinesPlugin InterwikiPlugin JQueryPlugin PreferencesPlugin SetGetPlugin SlideShowPlugin SmiliesPlugin TablePlugin TagMePlugin TinyMCEPlugin TwistyPlugin WatchlistPlugin WysiwygPlugin |
| modifyHeaderHandler | WysiwygPlugin |
| postRenderingHandler | PreferencesPlugin WysiwygPlugin |
| preRenderingHandler | InterwikiPlugin SmiliesPlugin TablePlugin |
The TWiki Plugin API
The Application Programming Interface (API) for TWiki plugins provides the specifications for hooking into the core TWiki code from your external Perl plugin module.Available Core Functions
The TWikiFuncDotPm module (lib/TWiki/Func.pm) describes all the interfaces available to plugins. Plugins should only use the interfaces described in this module.
Func.pm, you run the risk of creating security holes. Also, your plugin will likely break and require updating when you upgrade to a new version of TWiki.
Predefined Hooks
In addition to TWiki core functions, plugins can use predefined hooks, or callbacks, as described in thelib/TWiki/Plugins/EmptyPlugin.pm module.
- All but the initPlugin are commented out. To enable a callback, remove the leading
#from all lines of the callback.
Hints on Writing Fast Plugins
- Delay initialization as late as possible. For example, if your plugin is a simple syntax processor, you might delay loading extra Perl modules until you actually see the syntax in the text.
- For example, use an
evalblock like this:
eval { require IPC::Run }
return "<font color=\"red\">SamplePlugin: Can't load required modules ($@)</font>" if $@;
- For example, use an
- Keep the main plugin package as small as possible; create other packages that are loaded if and only if they are used. For example, create sub-packages of BathPlugin in
lib/TWiki/Plugins/BathPlugin/. - Avoid using preferences in the plugin topic; Define
$NO_PREFS_IN_TOPICin your plugin package as that will stop TWiki from reading the plugin topic for every page. Use Config.spec or preferences settings instead. (See details). - Use registered tag handlers.
- Measure the performance to see the difference.
Version Detection
To eliminate the incompatibility problems that are bound to arise from active open plugin development, a plugin versioning system is provided for automatic compatibility checking.- All plugin packages require a
$VERSIONvariable. This should be an integer, or a subversion version id.
- The
initPluginhandler should check all dependencies and return 1 if the initialization is OK or 0 if something went wrong.- The plugin initialization code does not register a plugin that returns 0 (or that has no
initPluginhandler).
- The plugin initialization code does not register a plugin that returns 0 (or that has no
-
$TWiki::Plugins::VERSIONin theTWiki::Pluginsmodule contains the TWiki plugin API version, currently 6.01.- You can also use the
%PLUGINVERSION{}%variable to query the plugin API version or the version of installed plugins.
- You can also use the
Security
- Badly written plugins can open huge security holes in TWiki. This is especially true if care isn't taken to prevent execution of arbitrary commands on the server.
- Don't allow sensitive configuration data to be edited by users. it is better to add sensitive configuration options to the
%TWiki::cfghash than adding it as preferences in the plugin topic.- Integrating with
configuredescribes the steps - TWiki:Plugins.MailInContrib
 has an example
has an example
- TWiki:Plugins.BuildContrib
 can help you with this
can help you with this
- Integrating with
- Always use the TWiki::Sandbox to execute commands.
- Always audit the plugins you install, and make sure you are happy with the level of security provided. While every effort is made to monitor plugin authors activities, at the end of the day they are uncontrolled user contributions.
Creating Plugins
With a reasonable knowledge of the Perl scripting language, you can create new plugins or modify and extend existing ones. Basic plug-in architecture uses an Application Programming Interface (API), a set of software instructions that allow external code to interact with the main program. The TWiki Plugin API provides the programming interface for TWiki. Understanding how TWiki is working at high level is beneficial for plugin development.Anatomy of a Plugin
A (very) basic TWiki plugin consists of two files:- a Perl module, e.g.
MyFirstPlugin.pm - a documentation topic, e.g.
MyFirstPlugin.txt
MyFirstPlugin topic. Other needed Perl code is best placed in a lib/TWiki/Plugins/MyFirstPlugin/ directory.
The plugin API handles the details of connecting your Perl module with main TWiki code. When you're familiar with the Plugin API, you're ready to develop plugins.
The TWiki:Plugins.BuildContribCreating the Perl Module
Copy filelib/TWiki/Plugins/EmptyPlugin.pm to <name>Plugin.pm. The EmptyPlugin.pm module contains mostly empty functions, so it does nothing, but it's ready to be used. Customize it. Refer to the Plugin API specs for more information.
If your plugin uses its own modules and objects, you must include the name of the plugin in the package name. For example, write Package MyFirstPlugin::Attrs; instead of just Package Attrs;. Then call it using:
use TWiki::Plugins::MyFirstPlugin::Attrs; $var = MyFirstPlugin::Attrs->new();
Writing the Documentation Topic
The plugin documentation topic contains usage instructions and version details. It serves the plugin files as FileAttachments for downloading. (The doc topic is also included in the distribution package.) To create a documentation topic:- Copy the plugin topic template from TWiki.org. To copy the text, go to TWiki:Plugins/PluginPackage
 and:
and: - enter the plugin name in the "How to Create a Plugin" section
- click Create
- select all in the Edit box & copy
- Cancel the edit
- go back to your site to the TWiki web
- In the JumpBox enter your plugin name, for example
MyFirstPlugin, press enter and create the new topic - paste & save new plugin topic on your site
- Customize your plugin topic.
- Important: In case you plan to publish your plugin on TWiki.org, use Interwiki names for author names and links to TWiki.org topics, such as TWiki:Main/TWikiGuest
 . This is important because links should work properly in a plugin topic installed on any TWiki, not just on TWiki.org.
. This is important because links should work properly in a plugin topic installed on any TWiki, not just on TWiki.org.
- Important: In case you plan to publish your plugin on TWiki.org, use Interwiki names for author names and links to TWiki.org topics, such as TWiki:Main/TWikiGuest
- Document the performance data you gathered while measuring the performance
- Save your topic, for use in packaging and publishing your plugin.
OUTLINE: Doc Topic Contents
Check the plugins web on TWiki.org for the latest plugin doc topic template. Here's a quick overview of what's covered: Syntax Rules: <Describe any special text formatting that will be rendered.>" Example: <Include an example of the plugin in action. Possibly include a static HTML version of the example to compare if the installation was a success!>" Plugin Settings: <Description and settings for custom plugin %VARIABLES%, and those required by TWiki.>" Plugin Installation Instructions: <Step-by-step set-up guide, user help, whatever it takes to install and run, goes here.>" Plugin Info: <Version, credits, history, requirements - entered in a form, displayed as a table. Both are automatically generated when you create or edit a page in the TWiki:Pluginsweb.>"
Packaging for Distribution
The TWiki:Plugins.BuildContribPlugin, ex: MyFirstPlugin.pm, and a documentation page with the same name(MyFirstPlugin.txt).
- Distribute the plugin files in a directory structure that mirrors TWiki. If your plugin uses additional files, include them all:
-
lib/TWiki/Plugins/MyFirstPlugin.pm -
data/TWiki/MyFirstPlugin.txt -
pub/TWiki/MyFirstPlugin/uparrow.gif[a required graphic]
-
- Create a zip archive with the plugin name (
MyFirstPlugin.zip) and add the entire directory structure from Step 1. The archive should look like this:-
lib/TWiki/Plugins/MyFirstPlugin.pm -
data/TWiki/MyFirstPlugin.txt -
pub/TWiki/MyFirstPlugin/uparrow.gif
-
Measuring and Improving the Plugin Performance
A high quality plugin performs well. You can use the TWiki:Plugins.PluginBenchmarkAddOnPublishing for Public Use
You can release your tested, packaged plugin to the TWiki community through the TWiki:Plugins- Post the plugin documentation topic in the TWiki:Plugins/PluginPackage
 :
: - enter the plugin name in the "How to Create a Plugin" section, for example
MyFirstPlugin - paste in the topic text from Writing the Documentation Topic and save
- enter the plugin name in the "How to Create a Plugin" section, for example
- Attach the distribution zip file to the topic, ex:
MyFirstPlugin.zip - Link from the doc page to a new, blank page named after the plugin, and ending in
Dev, ex:MyFirstPluginDev. This is the discussion page for future development. (User support for plugins is handled in TWiki:Support .)
.)
- Put the plugin into the SVN repository, see TWiki:Plugins/ReadmeFirst
 (optional)
(optional)

Recommended Storage of Plugin Specific Data
Plugins sometimes need to store data. This can be plugin internal data such as cache data, or data generated for browser consumption such as images. Plugins should store data using TWikiFuncDotPm functions that support saving and loading of topics and attachments.Plugin Internal Data
You can create a plugin "work area" using theTWiki::Func::getWorkArea() function, which gives you a persistent directory where you can store data files. By default they will not be web accessible. The directory is guaranteed to exist, and to be writable by the webserver user. For convenience, TWiki::Func::storeFile() and TWiki::Func::readFile() are provided to persistently store and retrieve simple data in this area.
Web Accessible Data
Topic-specific data such as generated images can be stored in the topic's attachment area, which is web accessible. Use theTWiki::Func::saveAttachment() function to store the data.
Recommendation for file name: - Prefix the filename with an underscore (the leading underscore avoids a name clash with files attached to the same topic)
- Identify where the attachment originated from, typically by including the plugin name in the file name
- Use only alphanumeric characters, underscores, dashes and periods to avoid platform dependency issues and URL issues
- Example:
_GaugePlugin_img123.gif
TWiki::Func::saveAttachment() function to store the data.
Recommendation for file names in plugin attachment area: - Prefix the filename with an underscore
- Include the name of the web in the filename
- Use only alphanumeric characters, underscores, dashes and periods to avoid platform dependency issues and URL issues
- Example:
_Main_roundedge-ul.gif
Integrating with configure
Some TWiki extensions have setup requirements that are best integrated into configure rather than trying to use TWiki preferences variables. These extensions use Config.spec files to publish their configuration requirements.
Config.spec files are read during TWiki configuration. Once a Config.spec has defined a configuration item, it is available for edit through the standard configure interface. Config.spec files are stored in the 'plugin directory' e.g. lib/TWiki/Plugins/BathPlugin/Config.spec.
Structure of a Config.spec file
The Config.spec file for an extension starts with the extension announcing what it is:
# ---+ Extensions # ---++ BathPlugin # This plugin senses the level of water in your bath, and ensures the plug # is not removed while the water is still warm.This is followed by one or more configuration items. Each configuration item has a type, a description and a default. For example:
# **SELECT Plastic,Rubber,Metal**
# Select the plug type
$TWiki::cfg{BathPlugin}{PlugType} = 'Plastic';
# **NUMBER**
# Enter the chain length in cm
$TWiki::cfg{BathPlugin}{ChainLength} = 30;
# **BOOLEAN EXPERT**
# Set this option to 0 to disable the water temperature alarm
$TWiki::cfg{BathPlugin}{TempSensorEnabled} = 1;
The type (e.g. **SELECT** ) tells configure to how to prompt for the value. It also tells configure how to do some basic checking on the value you actually enter. All the comments between the type and the configuration item are taken as part of the description. The configuration item itself defines the default value for the configuration item. The above spec defines the configuration items $TWiki::cfg{BathPlugin}{PlugType}, $TWiki::cfg{BathPlugin}{ChainLength}, and $TWiki::cfg{BathPlugin}{TempSensorEnabled} for use in your plugin. For example,
if( $TWiki::cfg{BathPlugin}{TempSensorEnabled} && $curTemperature > 50 ) {
die "The bathwater is too hot for comfort";
}
The Config.spec file is read by configure, which then writes LocalSite.cfg with the values chosen by the local site admin.
A range of types are available for use in Config.spec files:
| BOOLEAN | A true/false value, represented as a checkbox |
| COMMAND length | A shell command |
| LANGUAGE | A language (selected from {LocalesDir} |
| NUMBER | A number |
| OCTAL | An octal number |
| PASSWORD length | A password (input is hidden) |
| PATH length | A file path |
| PERL | A perl structure, consisting of arrays and hashes |
| REGEX length | A perl regular expression |
| SELECT choices | Pick one of a range of choices |
| SELECTCLASS root | Select a perl package (class) |
| STRING length | A string |
| URL length | A url |
| URLPATH length | A relative URL path |
| EXPERT | means this an expert option |
| M | means the setting is mandatory (may not be empty) |
| H | means the option is not visible in configure |
lib/TWiki.spec for many more examples.
Config.spec files for non-plugin extensions are stored under the Contrib directory instead of the Plugins directory.
Note that from TWiki 5.0 onwards, CGI scripts (in the TWiki bin directory) provided by extensions must also have an entry in the Config.spec file. This entry looks like this (example taken from PublishContrib)
# **PERL H**
# Bin script registration - do not modify
$TWiki::cfg{SwitchBoard}{publish} = [ "TWiki::Contrib::Publish", "publish", { publishing => 1 } ];
PERL specifies a perl data structure, and H a hidden setting (it won't appear in configure). The first field of the data value specifies the class where the function that implements the script can be found. The second field specifies the name of the function, which must be the same as the name of the script. The third parameter is a hash of initial context settings for the script.
TWiki:TWiki/SpecifyingConfigurationItemsForExtensionsMaintaining Plugins
Discussions and Feedback on Plugins
Each published plugin has a plugin development topic on TWiki.org. Plugin development topics are named after your plugin and end inDev, such as MyFirstPluginDev. The plugin development topic is a great resource to discuss feature enhancements and to get feedback from the TWiki community.
Maintaining Compatibility with Earlier TWiki Versions
The plugin interface (TWikiFuncDotPm functions and plugin handlers) evolve over time. TWiki introduces new API functions to address the needs of plugin authors. Plugins using unofficial TWiki internal functions may no longer work on a TWiki upgrade. Organizations typically do not upgrade to the latest TWiki for many months. However, many administrators still would like to install the latest versions of a plugin on their older TWiki installation. This need is fulfilled if plugins are maintained in a compatible manner.
if( $TWiki::Plugins::VERSION >= 1.1 ) {
@webs = TWiki::Func::getListOfWebs( 'user,public' );
} else {
@webs = TWiki::Func::getPublicWebList( );
}
Handling deprecated functions
From time-to-time, the TWiki developers will add new functions to the interface (either to TWikiFuncDotPm, or new handlers). Sometimes these improvements mean that old functions have to be deprecated to keep the code manageable. When this happens, the deprecated functions will be supported in the interface for at least one more TWiki release, and probably longer, though this cannot be guaranteed. When a plugin defines deprecated handlers, a warning will be shown in the list generated by %FAILEDPLUGINS%. Admins who see these warnings should check TWiki.org and if necessary, contact the plugin author, for an updated version of the plugin. Updated plugins may still need to define deprecated handlers for compatibility with old TWiki versions. In this case, the plugin package that defines old handlers can suppress the warnings in %FAILEDPLUGINS%. This is done by defining a map from the handler name to theTWiki::Plugins version in which the handler was first deprecated. For example, if we need to define the endRenderingHandler for compatibility with TWiki::Plugins versions before 1.1, we would add this to the plugin:
package TWiki::Plugins::SinkPlugin;
use vars qw( %TWikiCompatibility );
$TWikiCompatibility{endRenderingHandler} = 1.1;
If the currently-running TWiki version is 1.1 or later, then the handler will not be called and the warning will not be issued. TWiki with versions of TWiki::Plugins before 1.1 will still call the handler as required.
Warning: Can't find topic TWiki.TWikiNotificationOfChanges
Warning: Can't find topic TWiki.RenameTopic
Warning: Can't find topic TWiki.TWikiAdministration
Topic revision: r25 - 2001-08-30 - MikeMannix
- User Reference
- ATasteOfTWiki
- TextFormattingRules
- TWikiVariables
- FormattedSearch
- QuerySearch
- TWikiDocGraphics
- TWikiSkinBrowser
- InstalledPlugins
- Admin Maintenance
- Reference Manual
- AdminToolsCategory
- InterWikis
- ManagingWebs
- TWikiSiteTools
- TWikiPreferences
- WebPreferences
- Webs
-
 BusinessPractices
BusinessPractices
-
 Main
Main
-
 TWiki
TWiki
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback
Note: Please contribute updates to this topic on TWiki.org at TWiki:TWiki.TWikiDocumentation.